
News
- Check out this paper building on top of SlimGuard and enhancing it with fine grained hardware write-protection features (Intel SPP)
- Our SlimGuard paper has been accepted at Middleware 2019.
Awards
SlimGuard is awarded the artifacts available and artifacts evaluated functional badges.


You can download SlimGuard on Github.
SlimGuard is a secure dynamic memory allocator whose design is driven by memory efficiency. We redesign the security features of state-of-the-art allocators with memory efficiency in mind. SlimGuard protects against widespread heap-related attacks such as overflows, over-reads, double/invalid free, and use-after-free. Among other features, SlimGuard uses an efficient fine-grain size classes indexing mechanism and implements a novel dynamic canary scheme optimized for memory overhead reduction.
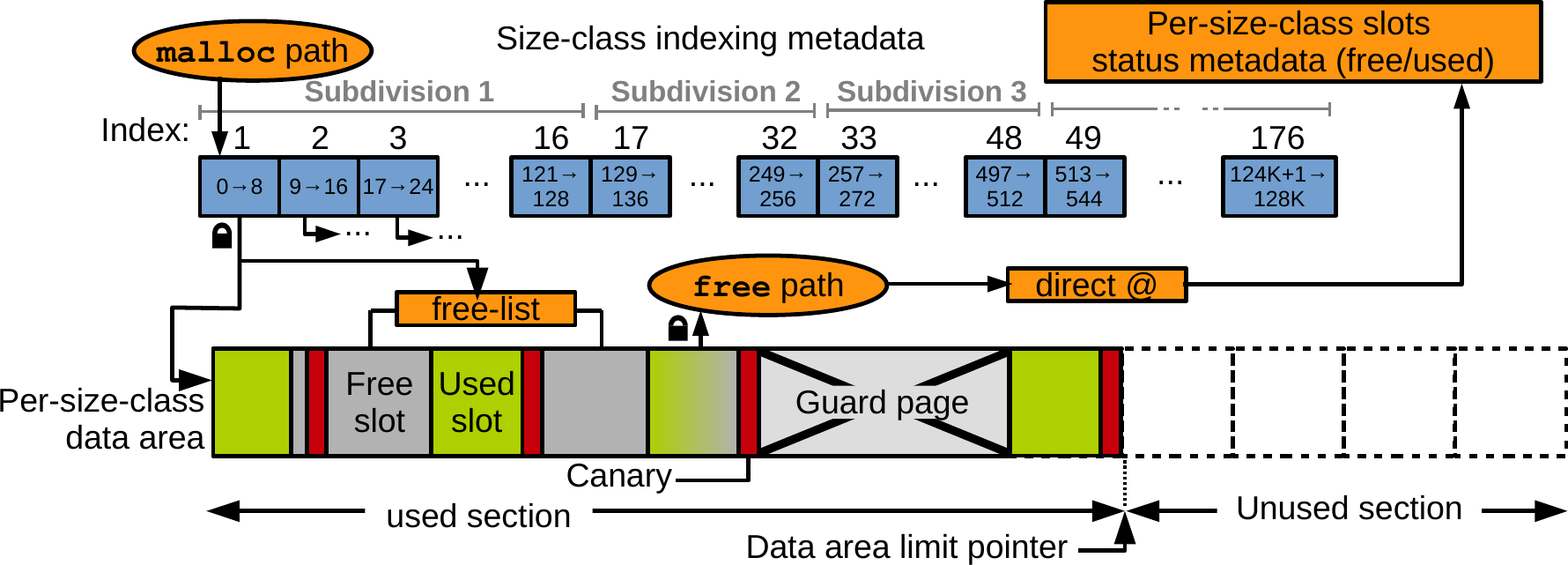
Design Principles
The security principles implemented within SlimGuard are the following: Randomized memory allocations with a significant entropy remove the capacity by the attacker to create a deterministic layout of objects on the heap. Over-provisioning protects in a probabilistic way against buffer overflows. Segregating metadata from data allows to pro- tect against metadata corruption-based attacks that are straightforward in systems storing metadata inline as headers with dynamically allocated objects. These metadata include in particular the state of each slot (free or used), checked upon free to protect against double-free-based attacks. Heap over- and under-flows are protected against with the use of heap canaries. Unmapped guard pages prevent heap buffer overflows and over-reads. Use-after-free attacks are made harder by using delayed randomized memory reuse and optionally destroying data on free.
Contact
Beichen Liu, Virginia Tech: beichen.liu at vt dot edu
Pierre Olivier, The University of Manchester: pierre.olivier at manchester.ac.uk
SlimGuard is an open-source project of the Systems Software Research Group at Virginia Tech.
SlimGuard is supported in part by ONR under grants N00014-16-1-2104 and N00014-18-1-2022. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this site are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of ONR.